Symptoms, Causes, and Risks
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. This interruption in breathing can significantly impact the quality of sleep and overall health. The most common symptom of sleep apnea is loud snoring, often accompanied by tiredness after a full night’s sleep.
Main Types of Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
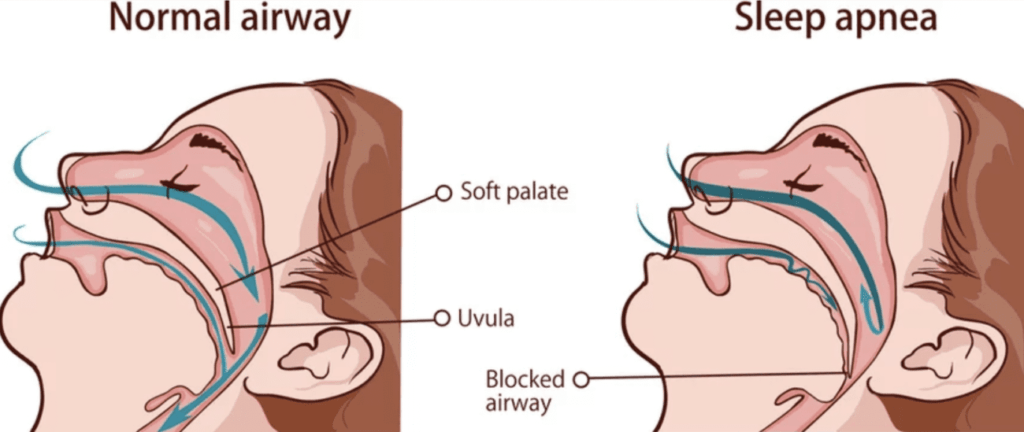
- Definition: The most common form of sleep apnea.
- Cause: Occurs when throat muscles relax excessively, blocking airflow into the lungs.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
- Definition: Less common than OSA.
- Cause: The brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Treatment-emergent Central Sleep Apnea (Complex Sleep Apnea)
- Definition: A condition where treatment for OSA, such as using continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), leads to the development of CSA.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Both OSA and CSA share several symptoms:
- Loud snoring.
- Episodes of breathing cessation during sleep, often noticed by another person.
- Gasping for air during sleep.
- Waking up with a dry mouth.
- Morning headaches.
- Insomnia or trouble staying asleep.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia).
- Difficulty paying attention while awake.
- Irritability and mood changes.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience symptoms like loud snoring, persistent fatigue, daytime sleepiness, or irritability, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Sleep apnea can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Throat Muscles Relaxation: Relaxation of the throat muscles leads to a blocked airway.
- Brief Awakenings: The brain briefly awakens you to reopen your airway, often resulting in snorting, choking, or gasping for air.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
- Signal Interruption: The brain fails to signal the breathing muscles, leading to disrupted sleep and shortness of breath.
Risk Factors
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Excess Weight: Obesity increases the risk of airway obstruction.
- Neck Circumference: Thicker necks may have narrower airways.
- Narrowed Airway: Inherited traits or enlarged tonsils/adenoids.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop OSA than women.
- Age: More common in older adults.
- Family History: Genetics can increase the risk.
- Substance Use: Alcohol, sedatives, and tranquilizers relax throat muscles.
- Smoking: Triples the risk of OSA.
- Nasal Congestion: Allergies or anatomical problems.
- Medical Conditions: Heart failure, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, etc.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
- Age: More common in middle-aged and older adults.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk.
- Heart Disorders: Conditions like congestive heart failure.
- Narcotic Pain Medicines: Use of opioids, especially long-acting ones.
- Stroke: Increases the risk of CSA.
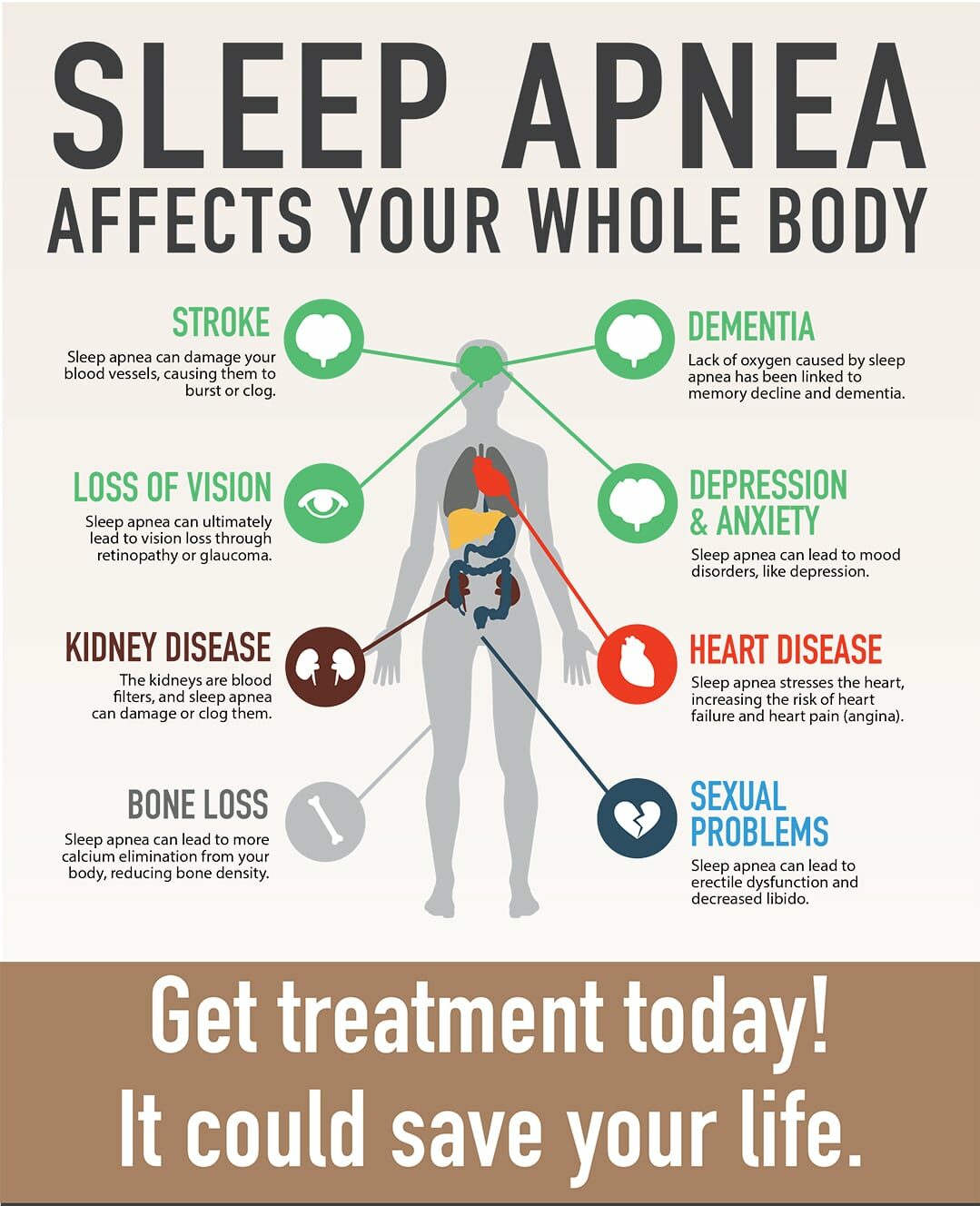
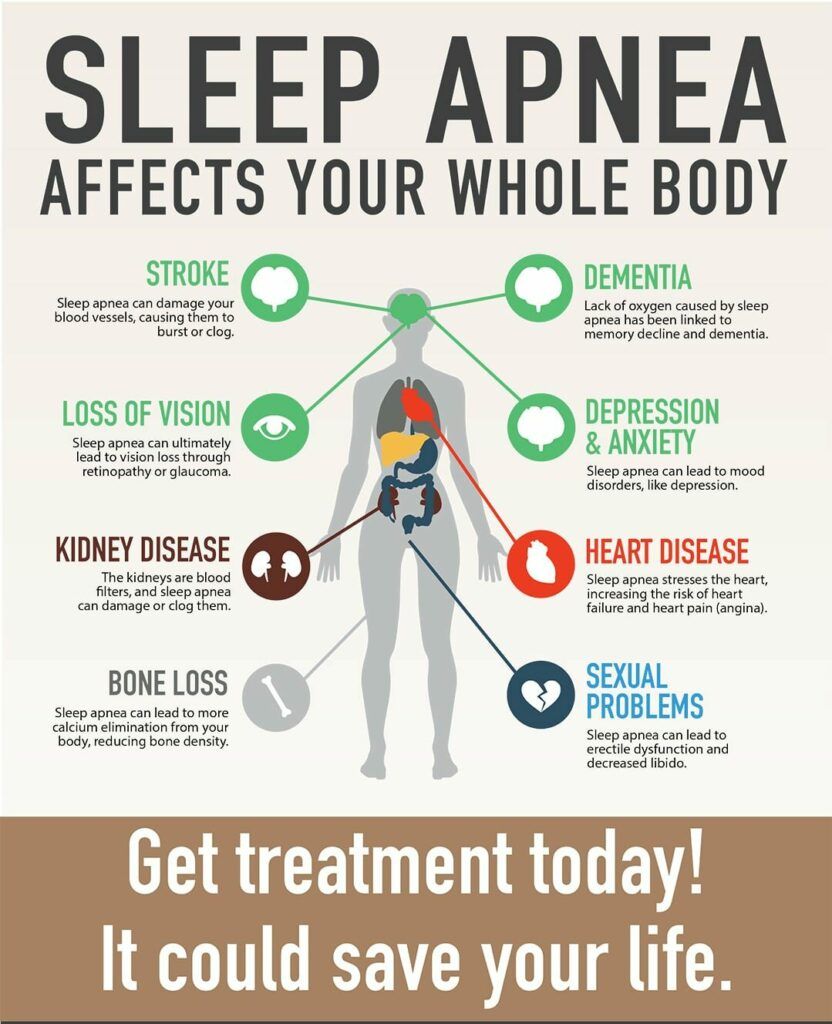
Complications of Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Daytime Fatigue: Severe drowsiness, irritability, and concentration issues.
- High Blood Pressure or Heart Problems: Increased risk of hypertension, heart attack, stroke, and arrhythmias.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Increased insulin resistance.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Includes high blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar, and increased waist circumference.
- Surgery Complications: Higher risk of breathing problems under sedation.
- Liver Problems: Abnormal liver function tests and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Sleep-deprived Partners: Partners may experience sleep issues due to loud snoring.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
- Fatigue: Severe drowsiness, irritability, and concentration issues.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Increased risk of irregular heart rhythms and worsening prognosis in heart disease.
Seeking Medical Advice and Treatment
It’s essential to see a healthcare provider if you suspect sleep apnea. Effective treatments can ease symptoms and prevent complications like heart problems. For instance, Mayo Clinic offers resources and books like “Future Care” to help manage sleep apnea.
Conclusion
Understanding sleep apnea and its symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. If you or a loved one experience symptoms like loud snoring, fatigue, or breathing interruptions during sleep, seek medical advice promptly. Proper management can significantly improve quality of life and overall health.
“This article is not meant to help cure or diagnose any sleep disorder/sleep apnea. It meant for educational purposes only. Always seek professional medical opinion before trying or changing anything like medication or exercise. (For Example)”